In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining optimal health and wellness is a top priority for many individuals. One essential component of overall well-being is ensuring an adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, including Vitamin B12. This crucial nutrient plays a significant role in various bodily functions, from nerve health to red blood cell production. In this article, we will delve into the abundant and diverse natural Vitamin B12 Foods, shedding light on how you can incorporate them into your diet for a healthier, more vibrant life.
Understanding Vitamin B12 Foods
Before we dive into the natural sources of Vitamin B12, let’s briefly understand why this vitamin is so vital for our bodies.
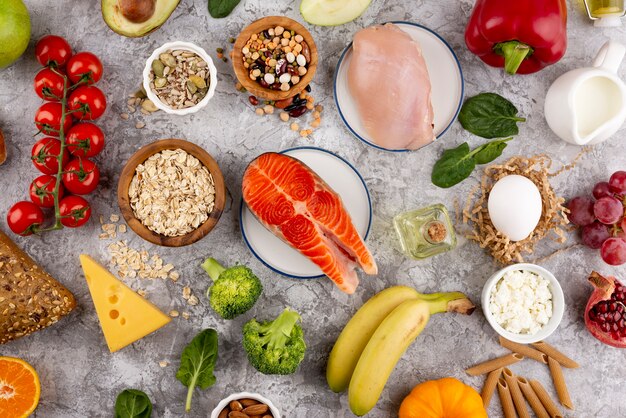

The Importance of Vitamin B12 Foods
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a pivotal role in several bodily functions:
- Nerve Health: Vitamin B12 is essential for maintaining a healthy nervous system, helping to prevent nerve damage and support optimal brain function.
- Red Blood Cell Production: It aids in the production of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
- DNA Synthesis: Vitamin B12 is involved in the synthesis of DNA, promoting proper cell growth and development.
Now that we understand why Vitamin B12 is essential let’s explore the diverse natural sources where you can obtain this vital nutrient.
Natural Food Sources of Vitamin B12
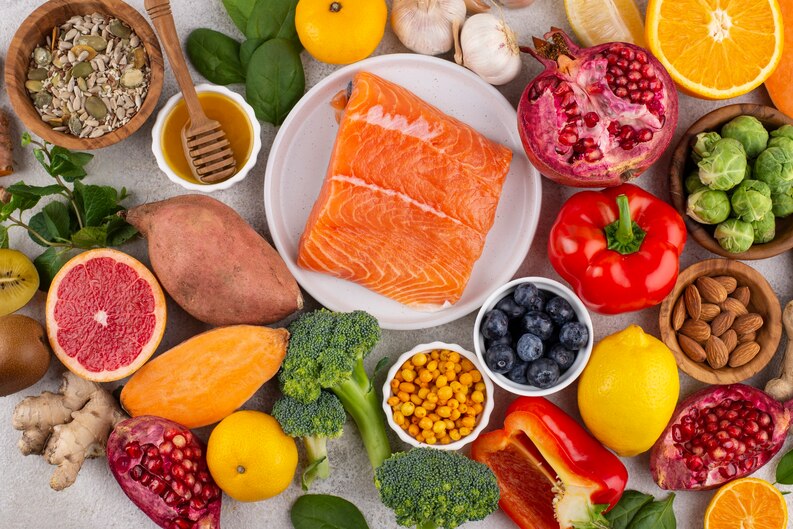

Animal-Based Sources
1.Meat
Meat, especially organ meats like liver and kidneys, is rich in Vitamin B12. Beef, pork, lamb, and poultry are excellent choices for those looking to increase their B12 intake.
2.Fish and Seafood
Fatty fish such as salmon, trout, and tuna are packed with Vitamin B12. Additionally, shellfish like clams and mussels are also excellent sources of this nutrient.
3.Dairy Products
Dairy enthusiasts can rejoice, as milk, yogurt, and cheese contain decent amounts of Vitamin B12. Opt for fortified dairy products for an extra B12 boost.
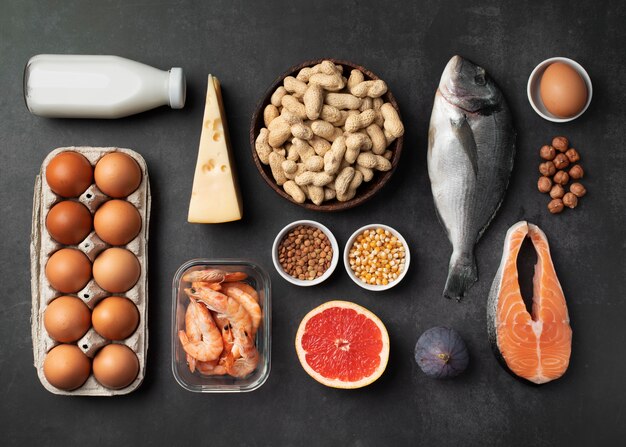
Plant-Based Sources
1.Fortified Foods
For vegetarians and vegans, fortified foods are a valuable source of Vitamin B12. Look for breakfast cereals, plant-based milk (like almond or soy), and nutritional yeast that have been fortified with B12.
2.Eggs
Eggs are one of the few plant-based sources of Vitamin B12. Including eggs in your diet can help meet your B12 requirements.
3.Algae and Seaweed
Certain types of algae and seaweed, such as nori and spirulina, contain small amounts of Vitamin B12. However, they may not provide enough to meet daily needs.
4.Supplements
In cases where obtaining enough Vitamin B12 through dietary sources is challenging, supplements are a convenient option. Speak to a healthcare professional to determine the right dosage for your needs.
5.B12 Injections
For individuals with severe B12 deficiencies, healthcare providers may recommend B12 injections for more immediate results.
Vitamin B12, essential for energy production and nerve function, plays a crucial role in overall health. It can be found in various animal-based foods and supplements. In my article “Meal Prep Under 10 Minutes” I discuss convenient ways to incorporate vitamin B12-rich foods into quick and nutritious meals, promoting well-being.
Incorporating Vitamin B12 into Your Diet
Now that you know where to find Vitamin B12, it’s essential to incorporate these sources into your diet regularly. Here are some practical tips:
- Include a variety of animal-based and plant-based sources to ensure a well-rounded B12 intake.
- Check food labels for fortification and B12 content.
- Consult a healthcare professional if you suspect a deficiency or need personalized guidance on B12 supplementation.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient for overall health and well-being. Exploring the abundant and diverse natural sources of Vitamin B12 can help you maintain optimal health and prevent potential deficiencies. By incorporating these sources into your diet wisely, you can ensure a vibrant and fulfilling life.
FAQs
A1: While it’s more challenging, it’s possible to obtain enough Vitamin B12 through fortified foods and supplements. Consult with a nutritionist for personalized advice.
A2: Common signs include fatigue, weakness, tingling in the hands and feet, and difficulty concentrating. A blood test can confirm a deficiency.
A3: Generally, Vitamin B12 supplements are safe. However, consult a healthcare professional for guidance, as excessive intake can lead to certain health issues.
A4: Yes, maintaining adequate Vitamin B12 levels can help combat fatigue and boost energy.
A5: It’s unlikely to overdose on Vitamin B12 from food alone, as excess amounts are usually excreted by the body. However, high-dose supplements should be used cautiously under medical supervision.





Leave a Reply